Managing Corporate Climate Risk: The Importance of Physical Climate Risk Assessment

As we journey further into the 21st century, the realities of climate change are becoming increasingly impossible to ignore. As such, corporate climate risk management is fast becoming a priority for companies globally. A crucial aspect of this process is physical climate risk assessment, a technique that dClimate is revolutionizing with open climate data and emerging technologies like AI and blockchain.
What is Corporate Climate Risk Management?
Corporate Climate Risk Management involves identifying, assessing, and prioritizing climate-related risks that a company faces. These risks can arise from a multitude of climate-related factors, such as extreme weather events or longer-term shifts in weather patterns that can disrupt operations or supply chains.
Understanding and managing these risks is vital to business continuity and resilience. Corporations that neglect climate risk management may face considerable operational, financial, and reputational damage.
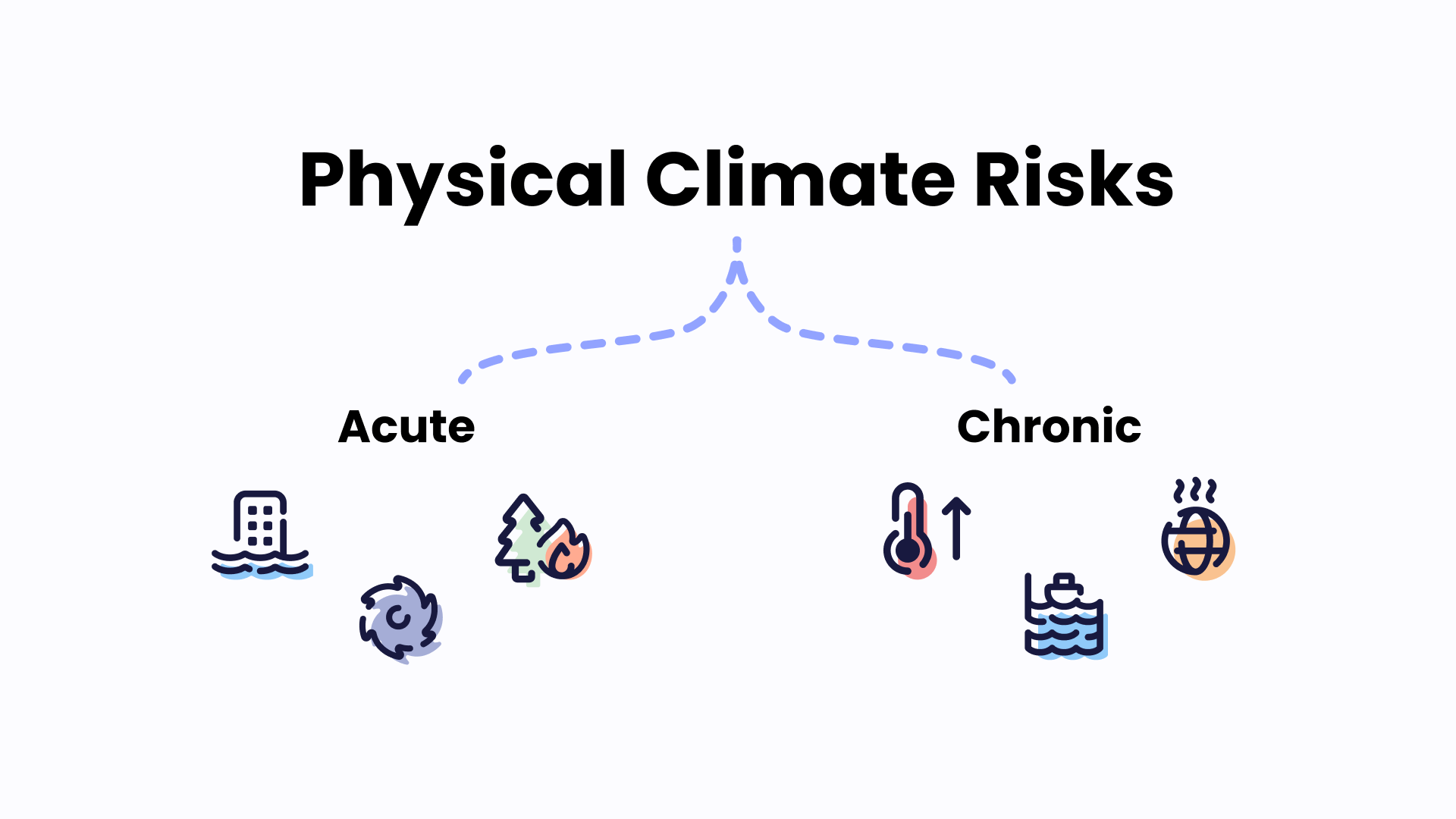
The Role of Physical Climate Risk Assessment
At the heart of corporate climate risk management lies physical climate risk assessment – a rigorous process that seeks to understand the potential risks posed by climate change to a company's tangible assets. These can include facilities, infrastructure, equipment, and supply chains.
The physical climate risks can take two forms.
- Acute risks, which stem from extreme weather events like floods, hurricanes, or wildfires.
- Chronic risks, associated with long-term shifts in climate patterns, such as steadily rising sea levels or gradually increasing temperatures.
The primary aim of a physical climate risk assessment is to discern what assets are at risk, the nature and severity of that risk, and the associated potential economic impact. The insights yielded from these assessments are invaluable, shaping strategic planning, informing risk management, and influencing pivotal corporate decisions.
Now, let's delve into how these assessments come to life. The process involves a series of interconnected stages, each bringing us closer to a comprehensive understanding of a company's climate risk profile.
Are you enjoying this content? Click here to sign up for our bi-weekly newsletter about climate data, regenerative finance, and climate risk so you won't miss our new articles.
How Does Physical Climate Risk Assessment Work?
Performing a physical climate risk assessment involves various stages. First, relevant climate data is collected and analyzed. This data can include historical weather records, climate projections, geographic information, and data about the company's physical assets.
Using this data, risk models are developed to simulate potential climate scenarios. These models help predict the impact of different climate events on the company's assets. Finally, the potential losses associated with these events are calculated, and mitigation strategies are developed. Further details about these phases are provided after the image below.
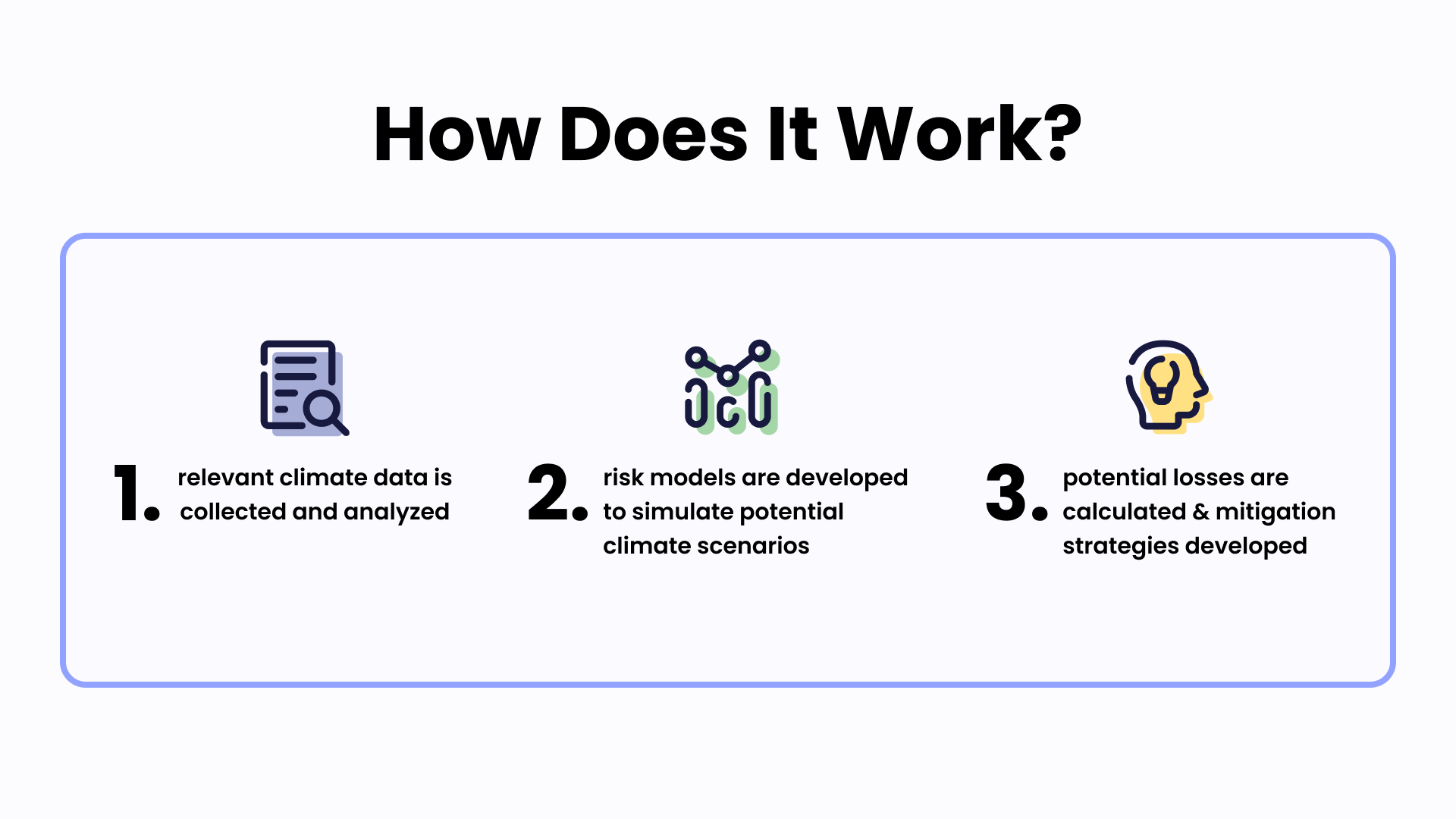
Step 1: Collection and Analysis of Climate Data
The first stage revolves around the collection and analysis of pertinent climate data. The scope of this data is extensive, encapsulating historical weather records, forward-looking climate projections, geographic information pertaining to the location of a company's assets, and detailed data about the physical assets themselves.
Step 2: Developing Risk Models
Following the data gathering phase, the next step involves the development of risk models. These models employ advanced statistical techniques and machine learning algorithms to simulate a broad array of potential climate scenarios. Each scenario represents a possible future state of the climate, underpinned by varying assumptions about greenhouse gas emissions, socio-economic factors, and other determinants of climate change. These models then predict the likely impact of different climate events on a company's assets under each scenario.
Step 3: Quantification of Potential Losses
The final stage involves the quantification of potential losses associated with these impacts. This might involve estimating repair or replacement costs for damaged assets, operational losses from business disruptions, or even broader economic impacts. Once these potential losses are calculated, they feed into the development of comprehensive mitigation strategies designed to manage and reduce the identified risks.
A Fundamental Pillar of Corporate Climate Risk Management
To summarize, physical climate risk assessment serves as a fundamental pillar of corporate climate risk management. It’s an intricate process that blends data science, climate science, and economic modeling, offering companies a clear lens through which to view their exposure to the rapidly changing climate. Through this, they can take informed steps towards ensuring their resilience in a world of accelerating climate change.
Why is it Important?
The importance of physical climate risk assessments within the sphere of corporate climate risk management is profound. These assessments serve as the bedrock of comprehending a company's susceptibility to the wide-ranging impacts of climate change, enabling an evidence-based approach to strategic planning and decision-making.

Proactive Risk Mitigation
A key reason these assessments are vital is their role in proactive risk mitigation. Historically, many businesses have adopted a reactive stance, responding to climate events as they occur. However, the scale and urgency of climate change necessitate a shift towards anticipation and preparedness. Physical climate risk assessments offer a means to predict potential vulnerabilities and impacts, thus enabling businesses to be prepared well in advance. By moving from reactive crisis management to proactive risk mitigation, companies can substantially reduce potential operational disruptions and financial losses.
Strategic Business Planning
Beyond immediate risk reduction, these assessments also contribute significantly to strategic business planning. They offer a clear picture of a company’s risk profile, highlighting areas where investment could fortify resilience. This could involve measures like strengthening infrastructure, diversifying supply chains, or even relocating vulnerable assets. With such valuable insights, companies can devise operational strategies that are not just resilient in the face of climate change, but also adaptive to its evolving landscape.
Corporate Transparency
Physical climate risk assessments also inform the growing need for corporate transparency about climate impacts. As shareholders, regulators, and the public demand greater disclosure of climate risks, these assessments provide the necessary data to fulfill these expectations. In line with guidelines from frameworks like the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), they can help companies articulate their climate risks and the measures they're taking to manage them. This transparency can enhance stakeholder trust, uphold a company's reputation, and even influence its market value.
Identifying Opportunities
Perhaps most excitingly, these assessments can illuminate new business opportunities emerging from the transition to a lower-carbon economy. They can identify areas where a company’s assets or operations are well-positioned to capitalize on climate-driven market shifts. This might involve developing new products or services that contribute to climate resilience or seizing opportunities in sectors poised for growth in a decarbonizing world.
The Role of Data
Data is the cornerstone of effective physical climate risk assessments. The quality, precision, and granularity of the data used can fundamentally shape the accuracy and value of the insights generated by these assessments. Thus, investing in comprehensive and reliable data sources becomes a top priority for businesses navigating the complex landscape of climate risk.
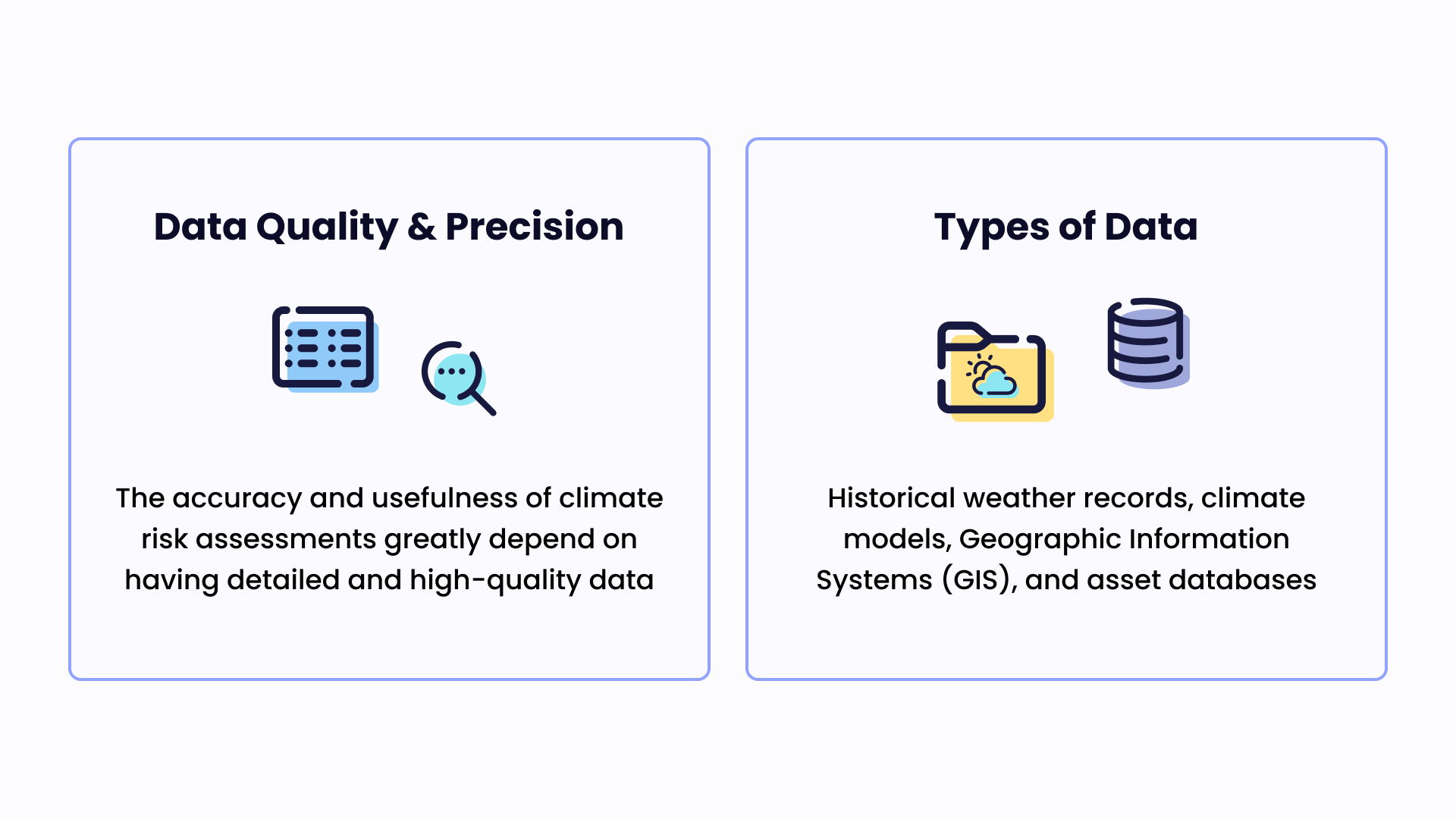
Types of Data
Several types of data are integral to physical climate risk assessments. Historical weather records, for example, provide invaluable context about past climate phenomena and trends. This data can help identify patterns and vulnerabilities that may be relevant to future climate scenarios.
Climate models and forecasts are another essential data type. These predictive tools can shed light on the range of potential climate scenarios that a company might face. By understanding these scenarios, businesses can anticipate the physical impacts they might encounter and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Geographical Information Systems (GIS) data provides another layer of granularity. By mapping assets and operations onto geographical locations, businesses can understand the spatial dimensions of their climate risks. For example, a business might identify locations that are particularly vulnerable to sea-level rise or extreme weather events.
Asset databases are also fundamental to these assessments. These databases should contain detailed information about a company's physical assets, such as their location, characteristics, and current conditions. This allows a company to estimate the potential impact of various climate scenarios on specific assets.
dClimate's Data Marketplace contains over 40 terabytes of free institutional-grade climate data that you can use to build climate risk models. Reading the documentation and joining our community on Discord is the easiest way to get started!
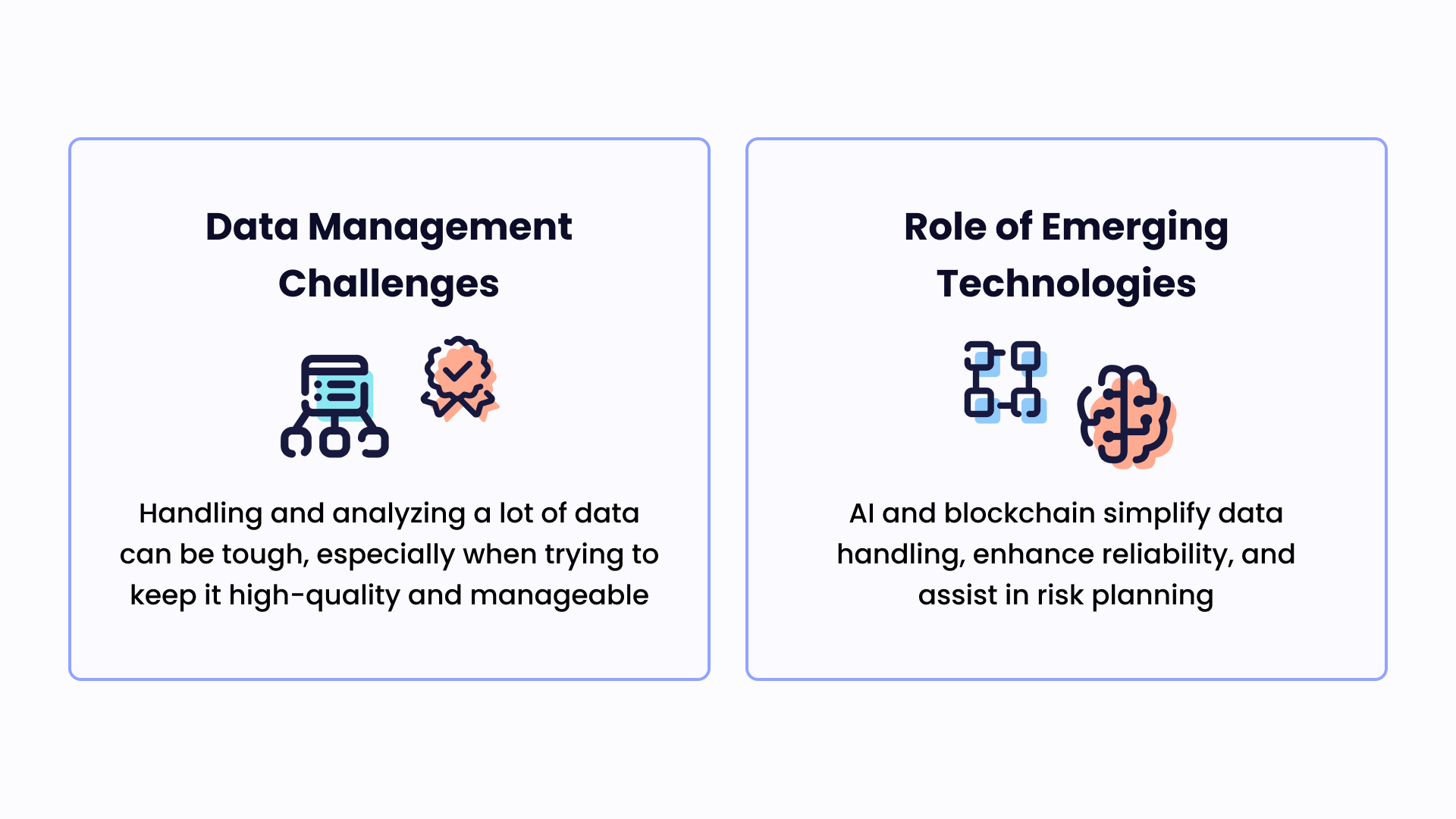
Data Management and Emerging Technologies
Despite the necessity of these types of data, the process of collecting, managing, and analyzing such vast quantities can be challenging. These challenges can range from ensuring data quality and integrity, managing data from different sources and formats, to storing and processing this data efficiently.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain are offering novel solutions to these challenges. AI, for instance, can automate the data processing and analysis, making it easier to extract actionable insights from the huge volumes of data. Meanwhile, blockchain can create immutable and transparent records of data transactions, ensuring data integrity and traceability.
In essence, data lies at the heart of physical climate risk assessments. It informs our understanding of potential future risks and enables the development of robust mitigation strategies. As we strive for a more resilient and sustainable future, the role of data, bolstered by cutting-edge technologies like AI and blockchain, will only grow in importance.

Our recent article about how AI can be used for climate action provides more depth and context.
Conclusion
While we still face many challenges in combating climate change, the intersection of these advanced technologies provides hope. They bring the capability for more informed decision-making, encouraging proactive climate action at a corporate level. By taking a data-driven approach to climate risk management, businesses can contribute to a more sustainable and resilient future, while also ensuring their own long-term success.
As we navigate this new era of corporate sustainability, it's important to remember that every business, no matter how large or small, has a role to play in mitigating climate change. By understanding and addressing our climate risks, we can collectively create a more sustainable, resilient world for future generations. The future will undoubtedly present challenges, but with knowledge, foresight, and innovation, we are well-equipped to meet them head on.
Do you want to learn more about the decentralized and open climate data ecosystem we are building?
- Explore our Data Marketplace with over 40 TB of free climate data
- Visit our Website, Blog, REST API and Documentation
- Sign up for our bi-weekly Newsletter
- Join the Community: Twitter | LinkedIn | Discord | Telegram | YouTube


